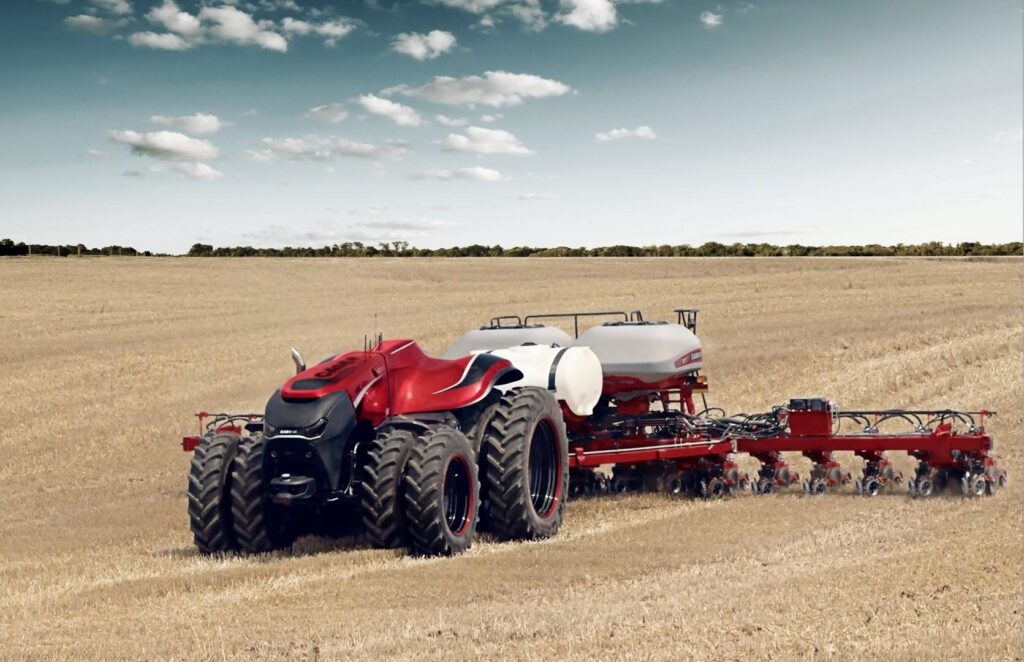
The emergence of autonomous tractors is fundamentally transforming the dynamics of global cargo transportation. As traditional logistics models evolve, these self-driving vehicles are streamlining operations at ports, warehouses, and distribution centers worldwide.By eliminating human operators, autonomous tractors offer continuous operation capabilities while reducing labor costs and human error in cargo handling processes. This technological advancement represents a notable shift in how goods move through the global supply chain, promising increased efficiency and reliability in international trade flows. The agricultural and logistics sectors are witnessing a revolutionary transformation as autonomous tractors integrate seamlessly into global supply chains. These self-driving machines, equipped with advanced AI systems and precision technology, are fundamentally altering how goods move from farms to distribution centers and ultimately to consumers worldwide.
these smart tractors utilize refined GPS navigation, computer vision, and sensor arrays to operate independently, working around the clock to maintain efficient cargo movement. Their implementation has reduced labor dependencies while concurrently increasing operational efficiency by up to 35% in early adoption cases.
The integration of autonomous tractors into existing logistics networks has created new opportunities for streamlined cargo handling. These vehicles can automatically load and unload containers, coordinate with warehouses, and synchronize with other transportation modes, establishing a more fluid supply chain ecosystem.
major manufacturers have developed specialized autonomous tractor models designed specifically for port operations and inland cargo terminals.These units feature enhanced lifting capabilities, automated coupling systems, and real-time communication protocols that allow them to interact with shipping management systems and other autonomous vehicles.
The impact on global trade is notably notable in agricultural regions,where autonomous tractors serve dual purposes: harvesting crops and managing their subsequent transportation. This dual functionality has reduced transfer times between harvest and shipping by approximately 40%, contributing to fresher produce reaching international markets.
Weather-resistant sensors and robust navigation systems enable these machines to operate in various environmental conditions, ensuring consistent cargo movement regardless of visibility or time of day. This capability has proven especially valuable in maintaining supply chain continuity during adverse weather conditions that typically impede traditional operations.
The economic implications extend beyond operational efficiency. Insurance companies have begun offering preferential rates for cargo handled by autonomous tractors, citing reduced human error and improved safety records. This financial incentive has accelerated adoption rates among logistics providers and agricultural enterprises.
Data analytics platforms integrated with autonomous tractor systems provide real-time cargo tracking and predictive maintenance scheduling.This integration has reduced unexpected downtime by 60% compared to traditional tractor operations, ensuring more reliable cargo flow across global supply routes.
Environmental benefits have emerged as an additional advantage, with autonomous tractors demonstrating 25% lower fuel consumption through optimized routing and more efficient operation patterns. This reduction in fuel usage has contributed to decreased carbon emissions in the logistics sector.
the technology continues to evolve, with manufacturers introducing new features such as swarm coordination capabilities and advanced obstacle detection systems. These improvements further enhance the role of autonomous tractors in maintaining smooth global cargo operations and strengthening international supply chain resilience.